Introduction:
Architectural Intent First, Tools Second
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is not a product — it is a converged infrastructure framework. It standardizes the full software-defined data center stack through automated lifecycle management, policy-driven operations, and intrinsic security.
Designing and deploying VCF from scratch is a high-stakes operation, particularly when disaster recovery (DR) is not an afterthought, but a built-in objective. This article captures the real-world implementation strategy for VCF 4.x+ including its integration with Site Recovery Manager (SRM) and vSphere Replication, covering both stretched and active/passive designs.
1. VCF Architecture – Core Principles
a. VCF Domains:
- Management Domain: Dedicated for infrastructure services (vCenter, NSX-T, SDDC Manager, vSAN, etc.)
- Workload Domains (WLD): Application/service boundaries — each domain gets its own vCenter, NSX, and vSAN if needed.
b. Integrated Stack:
- vSphere for compute
- vSAN as the native storage layer
- NSX-T for network virtualization and security
- SDDC Manager for lifecycle automation, updates, and configuration drift enforcement
c. Deployment Toolchain:
- Cloud Builder Appliance initiates the bring-up of the management domain using imaging bundles and config JSON.
- LCM via SDDC Manager handles version control, upgrade planning, and patch enforcement across all components.
2. Pre-Deployment Design Considerations
A. BOM + HCL Alignment
- All hardware (compute, NICs, SSDs, RAID controllers) must be listed in the VCF-certified BOM and VMware HCL.
b. Networking
- L2/L3 VLANs: Isolate Management, vMotion, vSAN, NSX overlay, and Edge uplinks
- MTU 9000 is mandatory end-to-end
- Redundant physical switches with LAG or vPC
c. NTP, DNS, Certificates
- Internal or external DNS must resolve FQDNs pre-deployment
- All services must be time-synced (NTP) or drift will break SDDC Manager functionality
- Use custom signed certs or deploy with VMCA and replace post-implementation
3. Implementation Workflow (Phased)
a. Phase 1: Imaging
- Prepare ESXi hosts with matching firmware
- Use Imaging bundle from VMware or vLCM JSON profile
b. Phase 2: Management Domain Bring-Up
- Deploy Cloud Builder
- Validate JSON config (cluster name, IPs, FQDNs, domain, NTP, DNS, passwords)
- Deploy management VMs (vCenter, NSX-T Manager, SDDC Manager, vSAN Cluster)
c. Phase 3: Workload Domain Creation
- Use SDDC Manager to instantiate additional WLDs
- Choose vSAN vs NFS
- Automate network provisioning via NSX-T
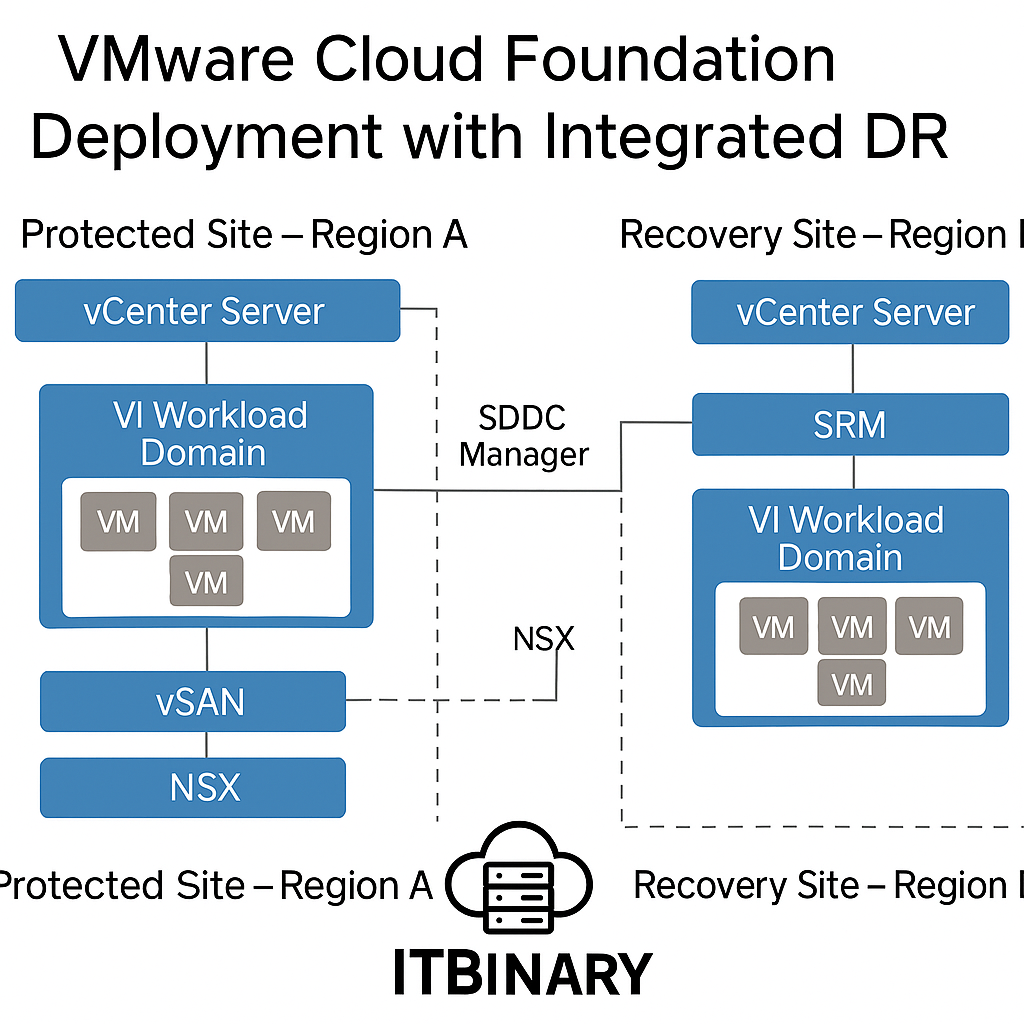
4. DR Design Integration
a. Option 1: SRM with vSphere Replication (Active-Passive)
- Two independent VCF instances (Primary & DR)
- SRM deployed on each management domain
- Replication via vSphere Replication or array-based (PowerMax, vVOLs, etc.)
- DNS failover required or use GSLB
- NSX-T must be manually extended or stretched
b. Option 2: Stretched Cluster (Active-Active)
- vSAN Stretched across two fault domains
- Witness appliance placed in 3rd location
- NSX-T segments stretched manually (beware of BUM traffic optimization)
- Metro clustering only valid with <5ms RTT
- Quorum must be preserved (split-brain risk mitigated)
5. Operationalization & Lifecycle
- Use SDDC Manager LCM bundles to enforce consistent patch levels
- Backup SDDC Manager, vCenter, NSX-T, and vSAN separately
- Use Aria Suite (vROps, vRLI, vRA) for monitoring, logging, and automated remediation
- DR testing via SRM Recovery Plans — validate with runbook automation
6. Real-World Issues to Avoid
| Issue | Impact | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete DNS resolution | Cloud Builder fails | Pre-stage all records incl. reverse lookup |
| Mixed firmware levels | Bring-up failure | Use HCL-validated vLCM image |
| Misaligned NSX VLANs | Overlay drops or fails to route | Pre-validate physical underlay mapping |
| Storage Policy mismatch | vSAN object inaccessible | Sync storage policies across WLDs |
📌 Final Thoughts
Deploying VMware Cloud Foundation from scratch is not just a task — it’s a commitment to architectural standardization, lifecycle automation, and design discipline. When disaster recovery is embedded into the blueprint, not added later, the result is a truly resilient SDDC.
VCF + DR Architecture Diagram
The following diagram illustrates the high-level design for a dual-region VCF deployment with integrated SRM-based disaster recovery
✍️ Author
Mohamed Omar — Infrastructure Architect and VMware Consultant with 17+ years in SDDC, vSAN, VCF, DR, and enterprise-grade virtualization architecture.


One of the most comprehensive blogs out there 👏